News Details
- admin
- 0 Comments
What are the Differences Between IVF and Natural Pregnancy?
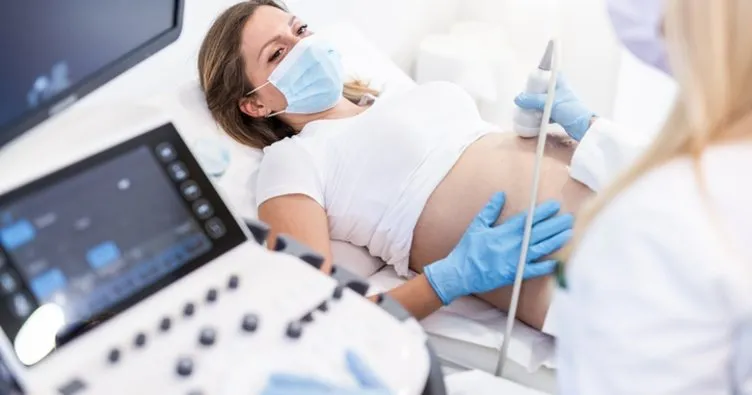
The journey to parenthood is deeply personal and can vary significantly from one couple to another. For many, the path to pregnancy follows a natural route, while for others, assisted reproductive technologies like IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) are necessary to help conceive. While both IVF and natural pregnancy result in the same end goal—a new life—there are key differences between the two processes. Understanding these differences can provide insight into the unique experiences of those undergoing IVF and help demystify the process for those considering this option. From the initial steps of conception to the emotional journey that accompanies each method, IVF and natural pregnancy come with distinct physical, emotional, and medical considerations. In this blog, we will explore these differences and shed light on what couples can expect from each path to parenthood.
The Conception Process: How IVF Differs from Natural Fertilization
The conception process through IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) differs significantly from natural fertilization, starting with the way the egg and sperm meet. In natural fertilization, the process begins when an egg is released from the ovary and travels down the fallopian tube, where it meets a sperm from the male partner. Fertilization then occurs naturally inside the body, and the embryo begins its development.
In contrast, IVF involves a more controlled and medicalized approach. The first step is ovarian stimulation, where the woman is given hormone injections to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs. Once the eggs are mature, they are retrieved from the ovaries in a procedure called egg retrieval. The retrieved eggs are then fertilized in a laboratory using sperm, either from the partner or a donor. After fertilization, the embryos are cultured in the lab, and the best quality embryos are selected to be transferred into the woman’s uterus. The entire process is monitored closely by fertility specialists to optimize the chances of a successful pregnancy.
While both methods ultimately aim to achieve pregnancy, IVF bypasses the natural processes of ovulation, fertilization, and embryo implantation, and instead uses medical interventions at each stage to help overcome infertility issues.
Hormonal Treatments in IVF vs. Natural Conception
Hormonal treatments play a significant role in IVF, but they are not typically involved in natural conception. In natural conception, a woman’s body follows its natural menstrual cycle, with hormones such as estrogen and progesterone regulating ovulation, fertilization, and early pregnancy. Each month, a single egg is released from the ovary, and if it is fertilized by sperm, pregnancy may occur.
In contrast, IVF involves a series of hormonal treatments to increase the chances of successful conception. To start, women undergoing IVF are usually given hormone injections to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs rather than the single egg produced during a natural cycle. This stimulation helps ensure that more eggs are available for fertilization, increasing the likelihood of creating viable embryos. Hormones like FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) and LH (luteinizing hormone) are commonly used for ovarian stimulation, while hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) is administered to trigger ovulation at the right time.
Following egg retrieval, additional hormonal treatments, such as progesterone supplements, are often prescribed to help prepare the uterus for embryo implantation and support early pregnancy. These hormonal treatments are a key difference between IVF and natural conception, as they help regulate and control the fertility process in IVF, whereas, in natural conception, the body’s hormones naturally guide each step of the reproductive cycle.
Monitoring and Medical Support: IVF Pregnancy vs. Natural Pregnancy
Monitoring and medical support during pregnancy can differ significantly between IVF and natural pregnancies. In a natural pregnancy, the process is largely managed by the body’s natural hormonal rhythms, with routine medical check-ups being the primary form of monitoring. These appointments typically focus on tracking fetal development, maternal health, and addressing any complications as they arise. Most women with a natural pregnancy will have regular ultrasounds, blood tests, and screenings, but the overall monitoring tends to be less frequent unless issues occur.
In contrast, IVF pregnancies often require more intensive monitoring and medical support due to the complex nature of the assisted reproductive process. From the initial stages of IVF, medical professionals closely track hormone levels to ensure proper embryo development and implantation. Once pregnancy is achieved, IVF patients typically undergo more frequent ultrasounds and blood tests in the early weeks to confirm the health of the pregnancy and ensure proper fetal growth. Additionally, some IVF pregnancies may require medication or hormone supplements to support the pregnancy, particularly in the first trimester, as the body may need extra support after the artificial fertilization process. The higher frequency of visits and medical intervention in IVF pregnancies is designed to monitor the unique circumstances and challenges that come with assisted conception, ensuring the best possible outcomes for both mother and baby.
Success Rates and Challenges: Comparing IVF and Natural Pregnancy
Success rates and challenges can vary significantly between IVF and natural pregnancies, with each path presenting its own set of factors that influence outcomes. In a natural pregnancy, success largely depends on factors such as age, overall health, and fertility. For many couples, conception occurs without medical intervention, but it can take time, especially as age increases. Natural pregnancies can also be affected by underlying health conditions or lifestyle factors that may reduce fertility.
On the other hand, IVF offers a more controlled and medically assisted approach, often providing a higher chance of pregnancy for couples facing infertility. Success rates for IVF depend on various factors, including the woman’s age, the quality of the eggs and sperm, the health of the uterus, and the clinic’s expertise. For women under 35, IVF success rates can range between 40-50%, but this decreases with age, especially after 40. However, IVF can still be a successful option for many couples, particularly when other treatments have failed.
While IVF may provide a higher success rate in certain cases, it also comes with unique challenges, including the emotional and financial stress associated with the process. The physical demands of hormone treatments, the risks of multiple pregnancies, and the emotional rollercoaster of failed attempts are just a few of the hurdles that IVF patients may face. Natural pregnancies, while often less medically intensive, can also present challenges, such as miscarriages or complications that arise unexpectedly.
Ultimately, the success and challenges of both IVF and natural pregnancies depend on the individual circumstances of each couple, and both paths require careful consideration and medical guidance.

Leave a comment